One paper has been accepted to Automation in Construction
Recently, a paper of us, named 'Enhanced Vision-based 6-DoF Pose Estimation for Robotic Rebar Tying', has been accepted to Automation in Construction whose impact factor reached at 11.5 scores in 2025 (SCI Q1).
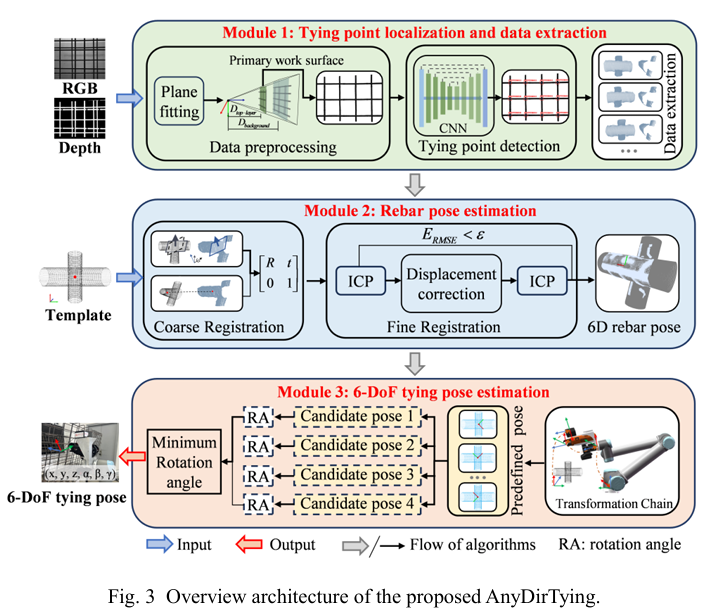
Abstract: Rebar tying is a labor-intensive and time-consuming task that involves repeatedly securing rebar intersections. While rebar tying robots have been developed to automate this process, most research focuses on tying point localization for horizontal ties, neglecting the 6 degrees of freedom (DoF) tying pose estimation required for reinforcement skeletons with rebar planes in various directions. This paper presents an any-direction robotic rebar tying method (AnyDirTying) for 6 DoF tying pose estimation. First, a deep learning-based keypoint detection algorithm extracts point clouds from rebar intersections. Next, a coarse-to-fine point cloud registration method is developed to improve the accuracy and stability of rebar pose estimation. Finally, a symmetry-aware tying strategy based on the minimum rotation angle is designed to optimize the tying pose and shorten the motion path. The proposed AnyDirTying enables flexible, accurate, and efficient tying pose estimation, expanding the applications of robotic rebar tying and reducing reliance on manual labor.
Keywords: Rebar tying; Any direction; 6-DoF tying pose; point cloud registration; Symmetry-aware
Mi Liu, Jingjing Guo, Lu Deng, Songyue Wang, Huiguang Wang
Automation in Construction, Impact Factor: 11.5 (SCI, Q1)
[Demo]

Automation in Construction is an international journal for the publication of original research papers. The journal publishes refereed material on all aspects pertaining to the use of Information Technologies in Design, Engineering, Construction Technologies, and Maintenance and Management of Constructed Facilities.
